On-line Partial Discharge Testing on Rotating Machines
Rotating machine failures stemming from insulation breakdown can result in catastrophic damage to your equipment. That’s why early detection of potential insulation failures is essential to maintaining healthy rotating machines. On-line partial discharge testing is a powerful tool you can use to assess machines while in operation to prevent high costs associated with equipment failure.
One of the major factors contributing to shortened lifetimes of high voltage generators and motors is deterioration of stator winding insulation. For decades, on-line PD measurement has been recognized as a reliable method of assessing stator insulation condition to forewarn plant personnel of possible machine failures. Once considerable PD activity is detected, assessment of the stator insulation condition can be made by analyzing PD data.
PD testing can also be used as part of a comprehensive on-line condition-based maintenance program. For this purpose, three PD couplers are permanently installed at the isolated phase bus of a generator. A PD measurement instrument collects PD data during generator operation. The stator insulation condition can then be evaluated through PD data analysis. A 2nF coupler, which is much more sensitive than an 80pF coupler, can effectively monitor more stator windings. Figure 1 shows that the three couplers were installed in a generator.
An example of the PD pattern in Figure 2 indicates partial discharges were at the overlap area of the semi-conductive coating and stress grade coating, i.e. the slot exit, as shown in Figures 3.

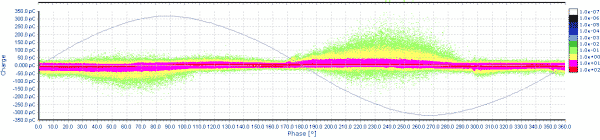 |

The following is a list of insulation defects identified by on-line PD testing:
- Damages of semi-conductive coating
- Loose stator coils or bars
- Winding contamination, oil, dirt, water
- Insulation delamination
- Damages of overlap area of semi-conductive coating and stress grade coating
- Voids within the stator insulation
- Phase-to-phase partial discharges
- Foreign metal objects on stator winding
- PD from insulators of IPB
- PD from PT and CT
- PD from terminal connections